As one of the most prominent cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, Salesforce is renowned for its flexibility and robust features, enabling businesses to manage customer data and interactions efficiently. However, to truly maximize Salesforce’s potential, it is crucial to understand Salesforce execution steps.
The order of execution is a vital aspect of Salesforce, referring to the sequence of events that transpire when a user performs a DML or triggers automation in Salesforce. This order defines the platform’s processing rules when handling a user’s request. Comprehending the Salesforce Order of Execution is essential for architects, developers, administrators, and anyone working with Salesforce.
In this blog, we will delve into the Salesforce Order of Execution, its various stages, and its impact on the platform’s behavior.
What is the Order of Execution in Salesforce?
The order of execution refers to the sequence of events that Salesforce follows when processing a user’s request. Every time a user interacts with Salesforce, the platform follows rules to process their request. These rules are predefined and determine how Salesforce will handle the user’s input. The order of execution plays a vital role in determining the outcome of the user’s request.
Understanding the Salesforce Order of Execution Stages:
Let’s take a closer look at each stage of the order of execution and understand how it operates.
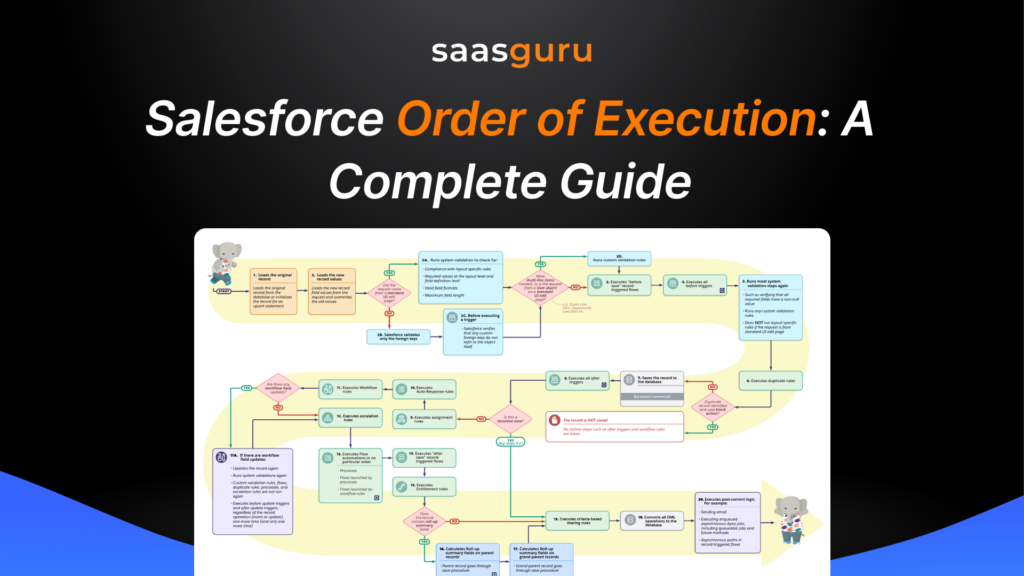
Before the events execute on the server, javascript validations are executed on the browser. After that events execute on a server in the below-given order.
Stage 1: Load the Data
Salesforce loads or initializes the record from the database. Salesforce also loads the new record with the provided new values by overriding the old values.
Stage 2: Identify the Request
Salesforce identifies the source of the request. The source can be standard UI pages, custom UI pages, SOAP Api or REST api. Based on the source of the request, different validation checks are performed.
Stage 3: Execute Record Triggered Flows
Salesforce executes Record Triggered flows which are created to run before the record is saved.
Stage 4: Execute Before Triggers
Salesforce executes all the Before triggers i.e. before insert or before update or before delete triggers. So, any logic written in the Before triggers will execute at this stage.
Stage 5: Validate the Data
Once the Before Triggers have been executed, Salesforce system validation mechanisms execute all the system and custom validations.
Stage 6: Duplicate Rules
After the validation, Salesforce runs the Duplicates rules on the record in context. The most important thing is if the Duplicate rules are configured with the Block action, then Order of execution will stop at this stage.
Stage 7: Save the Record
After the Duplicates rules, Salesforce will Save the record but will not commit it to the database. Record will only be committed when the record in context has successfully completed the order of execution without any failure.
Stage 8: Execute After Triggers
After the record is saved, Salesforce executes any After Triggers i.e. after insert, after update, after delete So, any logic written in the After triggers will execute at this stage
Stage 9: Execute Assignment Rules
If the record is an object that supports assignment rules, Salesforce executes the Assignment Rules at this stage. Assignment rules specify how records should be assigned to users or queues. These rules can be based on various criteria, such as record type, region, or priority.
Also Read – Lead Assignment Rules in Salesforce
Stage 10: Execute Auto-Response Rules
If the record is an object that supports auto-response rules, Salesforce executes the Auto-Response Rules at this stage. Auto-Response Rules specify how records should be automatically responded to, such as by sending an email or a text message.
Stage 11: Execute Workflow Rules – If workflow field updates occur:
- Perform another update on the record.
- Re-run system validations. Note that custom validation rules, flows, duplicate rules, processes, and escalation rules will not be re-executed.
- Execute before and after update triggers once more, irrespective of whether it’s an insert or update operation, but only once.
Stage 12: Escalations Rules
If the record is an object that supports Escalation Rules, Salesforce executes the Escalation Rules at this stage. Escalation rules specify how records should be escalated to higher authorities, such as managers or executives if they are not processed within a certain time frame.
Stage 13: Execute Flows
If the record is an object that supports Lightning Flows and Processes, Salesforce executes them at this stage. The order in which Flows will execute is as per system behavior and your configuration.
Stage 14: Execute After Record Triggered Flows
At this stage, Salesforce runs the record-triggered flows which are created to run after the record is saved.
Stage 15: Execute Entitlement Rules
If the record is an object that supports Entitlement Rules, Salesforce executes the Entitlement Rules at this stage.
Stage 16: Rollup Summary Fields
If the parent record or grand parent records contain rollup summary fields, then once the value is calculated the record goes through the save procedure cycle again.
Stage 17: Criteria-Based Sharing Rules
At this stage, Salesforce will check and execute all the Criteria Based Sharing Rules
for all the records in context to make sure the records are shared correctly.
Stage 18: Record Commit
After finishing all the above events on the server, Salesforce will finally commit the record in the database.
Stage 19: Post-Commit Logic
Once all the previous stages have been completed, Salesforce executes any Post-Commit Logic. Post-Commit Logic includes any custom code blocks developers have created to run after a record has been committed to the database. These code blocks can perform various actions, such as generating reports, updating external systems, or sending notifications, sending emails, invoking async jobs, etc.
Also Read – Salesforce Trigger Frameworks: A Comprehensive Guide
Why is Understanding the Order of Execution Important?
Understanding the order of execution is essential for anyone working with Salesforce. Here are some reasons why:
- Prevent Data Loss: Understanding the order of execution can help prevent data loss. For example, suppose a user updates a record and triggers a workflow rule that updates a field. In that case, it is essential to know the order of execution to prevent overwriting the user’s input.
- Improve Performance: Understanding the order of execution can help improve performance. For example, if a user performs an action that triggers multiple workflows, it is essential to know the order of execution to optimize the workflow’s performance.
- Ensure Compliance: Understanding the order of execution can help ensure compliance. For example, suppose a user performs an action that triggers a validation rule. In that case, it is essential to know the order of execution to ensure that the data entered by the user meets the specified criteria.
- Debugging: Understanding the order of execution can help with debugging. For example, if a user performs an action that results in an error, it is essential to know the order of execution to debug the error and fix the issue.
Important Considerations and Changes from Flow Behavior
When developing Salesforce triggers, it’s essential to be mindful of specific considerations and recent changes in flow behavior that can significantly impact how triggers operate within the Salesforce environment. These factors are critical for ensuring effective data processing and system performance.
1. Behavior of Trigger.old in Workflow Updates:
A key consideration in trigger logic is understanding how Trigger.old behaves during workflow updates. If a workflow rule updates a field after a user-initiated record change, Trigger.old retains the values from before the user update, not those altered by the workflow. For instance, if a workflow rule modifies a field post-user update, the value in Trigger.old during subsequent triggers will reflect the pre-user-update state, not the intermediate state post-workflow update.
2. Triggers in Partial DML Operations:
When a Data Manipulation Language (DML) operation allows partial success, triggers related to that operation fire with each attempt. Importantly, static variables within these triggers do not reset between attempts within the same transaction. This persistence is crucial for developers to understand when designing triggers for bulk operations and handling exceptions.
3. Execution Order of Multiple Triggers:
If there are multiple triggers on a single object for the same event, Salesforce does not guarantee their execution order. This uncertainty can lead to unpredictable results, especially if these triggers interact or depend on one another. Developers should consider this when creating multiple triggers for the same object event.
4. Changes in Flow Execution:
With newer Salesforce API versions (post 53.0), there’s a change in how after-save record-triggered flows execute concerning entitlements. In earlier versions, these flows would execute after entitlement rules. Awareness of this change is vital for those working with record-triggered flows and entitlement processes, as it affects the sequence of automation and data handling.
5. Complex Relationships and Execution Context:
For operations involving complex relationships, such as inserting non-private contacts linked to multiple accounts, the execution context and order can have nuanced behaviors. Developers should refer to Salesforce documentation specific to these use cases, like AccountContactRelation, for a deeper understanding.
6. Optimizing Opportunity Trigger Logic:
In scenarios involving Opportunity objects, especially when using before triggers to set fields like Stage and Forecast Category, there are unique considerations. Developers should familiarize themselves with the specific behaviors and best practices for Opportunity triggers to ensure correct functionality and data integrity.
By keeping these important considerations and changes in flow behavior at the forefront, Salesforce developers can design more efficient, reliable, and effective triggers. This approach not only enhances data processing accuracy but also contributes to overall system performance and stability within the Salesforce ecosystem.
Key Challenges and Solutions in Salesforce Order of Execution
While the Salesforce Order of Execution is designed to ensure smooth and predictable processing, developers and administrators often encounter challenges when managing complex automation. Understanding these challenges and their solutions can significantly improve system performance and reliability.
1. Challenge: Managing Automation Conflicts
When multiple automations like workflows, triggers, and record-triggered flows are active on the same object, conflicts can arise, causing unintended behavior.
Solution:
- Use Process Builder or Flows Strategically: Consolidate automations where possible to avoid overlap.
- Define Clear Precedence: Document the purpose of each automation to ensure clarity and reduce redundancy.
- Testing and Simulation: Test automations in isolated environments to identify and resolve conflicts.
2. Challenge: Recursive Trigger Execution
When a trigger updates a record that causes another trigger or automation to fire, it can lead to infinite loops or unnecessary processing.
Solution:
- Static Variables: Use static variables to track whether a trigger has already run within the current context.
- Avoid Direct Updates in After Triggers: Move record updates to Before Triggers to minimize recursion risks.
- Recursive Control Custom Settings: Implement custom settings to enable or disable specific automations dynamically.
3. Challenge: Governor Limit Exceedance
Complex processing can easily exceed Salesforce governor limits, such as SOQL queries, DML statements, or CPU time.
Solution:
- Bulkify Code: Ensure SOQL queries and DML statements are optimized for bulk processing.
- Query Selectively: Fetch only the fields required for the operation to minimize memory usage.
- Utilize Asynchronous Processing: Move heavy operations to Queueable or Batch Apex to distribute processing load.
4. Challenge: Debugging Multi-Stage Automation
Identifying the root cause of errors in a multi-stage execution process can be difficult, especially when multiple triggers or flows are involved.
Solution:
- Enable Debug Logs: Use debug logs to track execution steps and pinpoint issues.
- Transaction Monitoring: Monitor Apex Jobs and Flow Executions to identify problematic stages.
- Break Down Automation: Split complex automations into smaller, manageable parts for easier troubleshooting.
5. Challenge: Post-Commit Logic Performance
Post-commit logic, such as sending emails or invoking external APIs, can delay record processing or lead to errors if not properly optimized.
Solution:
- Use Asynchronous Methods: Move post-commit actions to Queueable or Future methods to handle them outside the main transaction.
- Monitor Queues: Regularly monitor the Apex Jobs queue to ensure post-commit actions are executed promptly.
- Optimize API Callouts: Implement retry mechanisms and efficient error handling for API integrations.
Summing Up
Understanding the Salesforce order of execution is crucial for any developer or administrator working with the platform. It’s like knowing the game’s rules before you start playing, and it can help you avoid any surprises along the way.
By keeping in mind the different phases of the order of execution and the specific actions that take place within each one, you can optimize your code and ensure that it runs smoothly and efficiently.
If you are interested in amplifying your Salesforce skills, consider enrolling in the Salesforce Training Bootcamp Program by saasguru. Become 3X Salesforce certified and job-ready with our comprehensive program. Our graduates have witnessed an impressive average salary hike of 112%, a testament to the effectiveness of our curriculum. Start your upskilling journey with us today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is the Salesforce order of execution important?
Salesforce’s execution sequence is key for ensuring smooth operations, preventing automation overlaps, enhancing efficiency, quickly resolving issues, and maintaining data accuracy.
2. How do you remember the order of execution in Salesforce?
To better grasp Salesforce’s sequence, use these strategies: create mnemonics from phase initials, draw charts or graphs for visualization, regularly review the sequence, gain hands-on experience with real scenarios, and use prompt cards or apps for periodic knowledge testing.
3. How does Salesforce process transactions in sequence?
The Salesforce transaction processing order ensures a structured and predictable flow of data manipulation and business logic execution, enabling precise control over how records are processed and ensuring data integrity.
4. Roles that require deep knowledge of Salesforce Order of Execution:
Architects, developers, and administrators must deeply understand the order of execution to build efficient, reliable, and scalable solutions within the Salesforce platform.
5. How does mastering Salesforce Execution Order impact Salesforce Developer roles?
By mastering the Salesforce Order of Execution, developers can optimize automation, prevent data inconsistencies, and ensure a high application performance, directly impacting their ability to deliver robust Salesforce solutions.